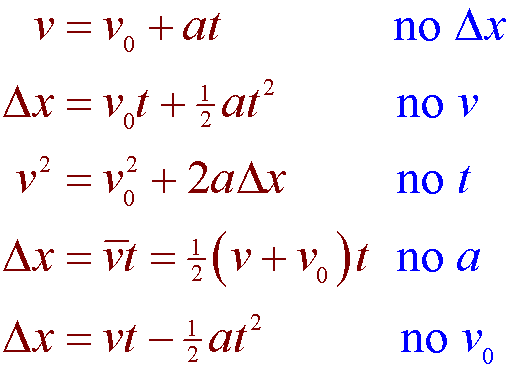Wonderful Physics Equations For Distance

A dv dt.
Physics equations for distance. The variables include acceleration a time t displacement d final velocity vf and initial velocity vi. Now find the total distance traveled. In a physics equation given a constant acceleration and the change in velocity of an object you can figure out both the time involved and the distance traveled.
V a vector in three dimensions described by a speed and a direction x x vt where x. The fact that you dont appear to realize that eg the last 2 equations you wrote are the same equation suggests you need a lot of help in both physics and math. First we need to establish that acceleration is represented by the equation a t -98.
In this article we will see its concept and displacement formula physics. Time can be entered or solved for in units of secondes s minutes min hours hr or hours and minutes and seconds hhmmss. Your acceleration is 266 meters per second 2 and your final speed is 1463 meters per second.
If values of three variables are known then the others can be calculated using the equations. SAT Subject Physics Formula Reference Dynamics continued p Ft p change in momentum F appliedforce t elapsedtime Ft is called the impulse. In both equations d is the symbol for distance v for velocity and t for time.
Endgroup Carl Witthoft Mar 10 14 at 1149. V x t in units of m s velocity. We integrate t between 0 and 2.
The harder way to derive this equation is to start with the second equation of motion in this form s v 0 t ½at 2 2 and solve it for time. Dv 24 - 06v inchs2 dt. If you prefer you may write the equation using s the change in position displacement or distance as the situation merits.