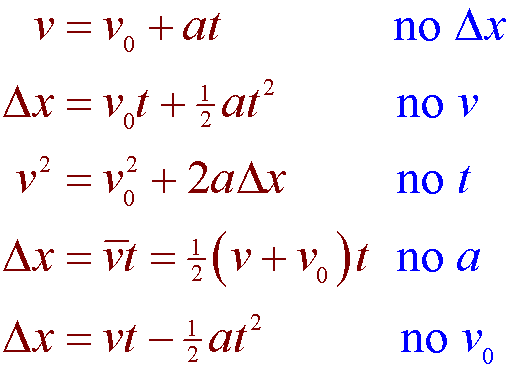Great Kinematics Equations Physics

You should work out the algebra to.
Kinematics equations physics. Building on what you have learned so far and what Galileo presented we have what my physics teacher Glenn Glazier liked to call the Five Sacred Equations of Kinematics for constant acceleration. The table below lists the given motion parameters. Equations of Motion 1 - Motion in a Straight Line Deep underground Carmen and Alexandra Lexi Luthor perform a top-secret science experiment.
Kinematic Equations for Linear Motion For constant acceleration ONLY To select the appropriate equation to solve a particular problem. Take the operation in that definition and reverse it. This video is an introduction to the kinematics equations with constant acceleration.
Three of the equations assume constant acceleration equations 1 2 and 4 and the other equation assumes zero acceleration and constant velocity equation 3. V v0 at v v 0 at. Kinematic equations can be applied to any motion for which the acceleration is constant.
The kinematic equations are simplifications of object motion. Why is the time interval now written as t If we know three of these five kinematic variables for an object under constant acceleration we can use a kinematic formula see below to solve for one of the unknown variables. The kinematic formulas are a set of formulas that relate the five kinematic variables listed below.
Kinematics equations are a set of equations that can derive an unknown aspect of a bodys motion if the other aspects are provided. The equations can be utilized for any motion that can be described as being either a constant velocity motion an acceleration of 0 mss or a constant acceleration motion. In these equations v is velocity x is position t is time and a is acceleration.
In this video Dan Fullerton provides a brief introduction to kinematic equations for solving motion problems in high school physics courses including Regents. 1 List what quantities are given - will be 3 2 List what is being asked for - will be 13 Find the equation in the table that contains all 4 involved quantities. Instead of differentiating velocity to find acceleration integrate acceleration to find velocity.