Amazing Chemistry Of Combustion

It is also known as burning.
Chemistry of combustion. Since we study all the hydrocarbons in organic chemistry the heat evolved by their combustion reaction is called heat of combustion of organic compounds. Combustion chemistry in the cylinder of an engine takes place in the gas phase. If you think about combustion in an engine with fuel it seems like a simple process but it is actually very complex Pratt said.
Combustion is considered an exergonic or exothermic chemical reaction. Since methane is made up of atoms of carbon and hydrogen the products of its combustion reaction are oxides of carbon. MORLEY 11 HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE As described in the Introductory Chapter attention was focused prior to 1961 mainly on the morphology of the cool-flame and ignition regions rates were followed by pressure change and essentially chemical techniques were used for product analysis.
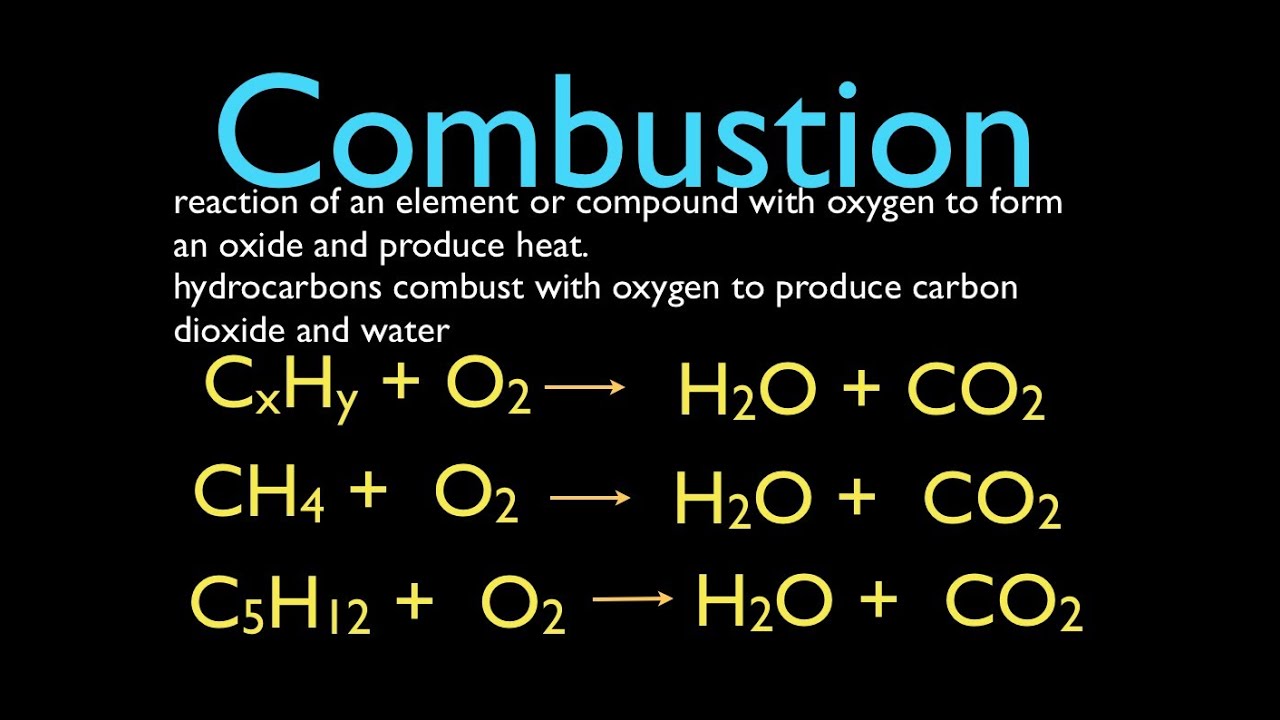
Most combustion reactions occur when hydrocarbons react with oxygen to form carbon monoxide and water. Introduction to Combustion Chemistry The gasoline-powered internal combustion engine takes air from the atmosphere and gasoline a hydrocarbon fuel and through the process of combustion releases the chemical energy stored in the fuel. A combustion reaction is a major class of chemical reactions commonly referred to as burning In the most general sense combustion involves a reaction between any combustible material and an oxidizer to form an oxidized product.
What is combustion in chemistry. During a combustion reaction the material reacts with oxygen from the air and contributes energy to the atmosphere as light and heat. Combustion is considered to be one of the first chemical reactions intentionally controlled by humans.
39 Combustion Analysis Video This project was preformed to supply Libretext authors with videos on General Chemistry topics which can be used to enhance their projects. Introduction to Physics and Chemistry of Combustion. 23 hours agoVolatile organic compounds VOCs which are made out of carbon and hydrogen atoms and exist as gases at room temperature include everyday fuels such as.
Combustion or burning is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel the reductant and an oxidant usually atmospheric oxygen that produces oxidized often gaseous products in a mixture termed as smoke. Combustion is a high-temperature exothermic heat releasing redox oxygen adding chemical reaction between a fuel and an oxidant usually atmospheric oxygen that produces oxidized often gaseous products in a. Individual reactions can be considered at the molecular level.