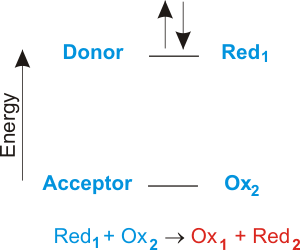
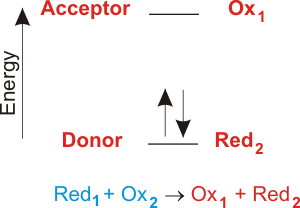
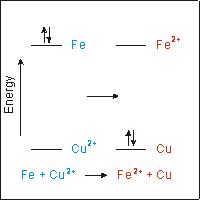
Impressive Electron Transfer Equation

Cytochromes are very similar to the structure of myoglobin or hemoglobin.
Electron transfer equation. Subsequent relaxation occurs to the intersection region at X 12 where further relaxation or intramolecular electron transfer give a. Explaining the electron transfer process The following video from the McGraw-Hill website shows what happens during a redox reaction at a molecular level. Electron transfer reactions are commonly described by the phenomenological ButlerVolmer equation which has its origin in kinetic theories.
Write the unbalanced equation in ionic form. The simplest reactions in solution chemistry are electron self-exchange reactions Equation 610 in which the reactants and products are the same the asterisk is used to identify a specific isotope. It is called working electrode.
The ButlerVolmer equation relates interfacial reaction rates to bulk quantities like the electrostatic potential and electrolyte concentrations. It is the energy required to displace the system an amount Q X B - X A without electron transfer. Separate the equation into two half reactions.
This is the energy required to transfer the electron from the bottom of the energy profile of the acceptor product state up to the energy profile of the acceptor state in the same nuclear configuration as the energy minimum of the donor state. D Asymmetric electron transfer α 01 If the interfacial voltage only biases one direction of a Faradaic reaction say the positive oxidation reaction α 0 and not. 4Al 3O 2 2Al 2 O 3 With oxidation numbers inserted as superscripts this reaction is written.
A short description of electron transfer in a REDOX reaction. A summary of the reactions in the electron transport chain is. Consider an electrolyte in which an inert or noble electrode is kept immersed.
610 A o x A r e d A r e d A o x. Consider the following redox equation. Balance atoms other than H and O.