Beautiful Decomposition Chemistry Formula

Describes the basics of decomposition reactions how to identify them predict the products and balance the chemical equation.
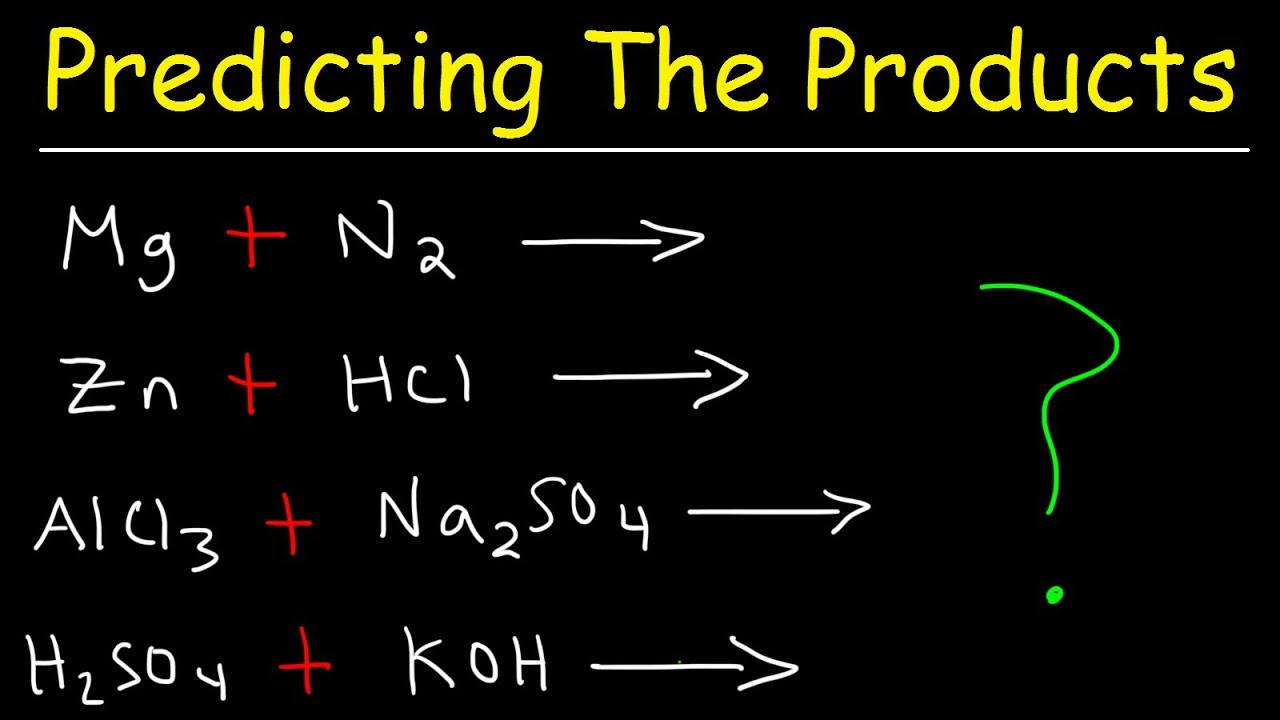
Decomposition chemistry formula. Decomposition in chemistry means breaking of a single reactant to form more stable products compared to the reactant. A decomposition reaction is a reaction in which a compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances. Two examples are also shown d.
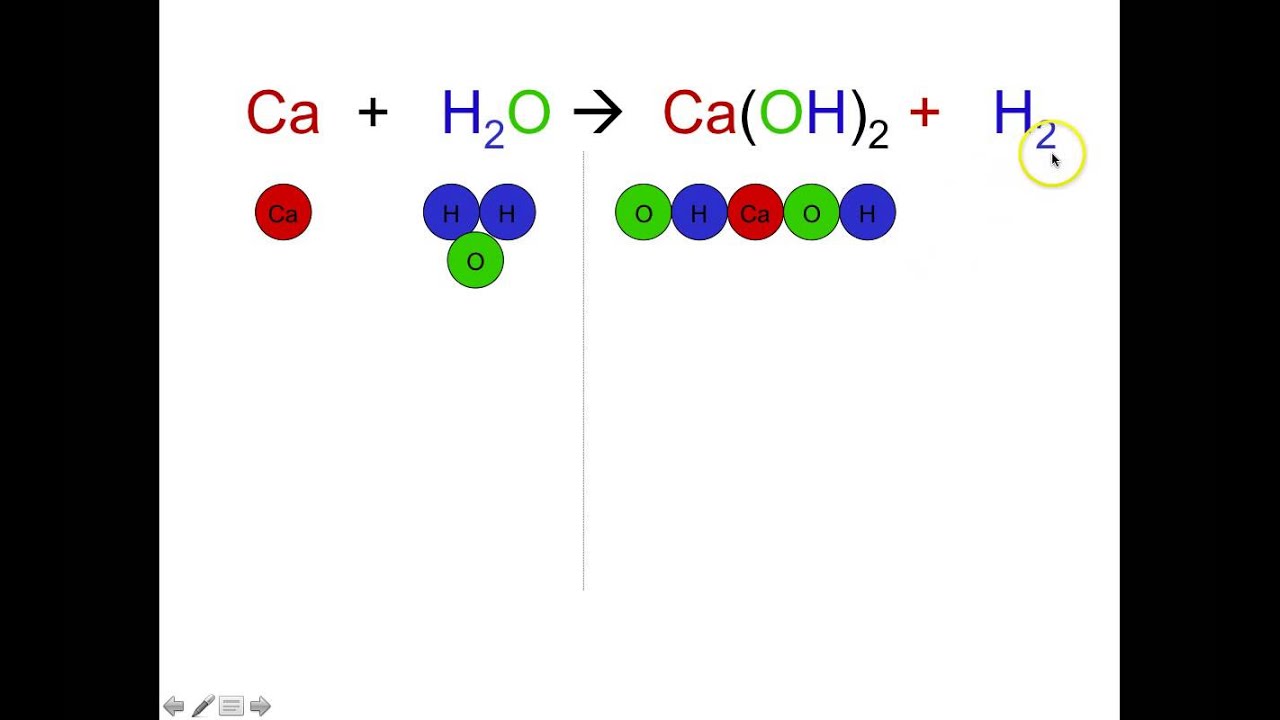
The breaking of chemical bonds requires the addition of energy usually in the form of heat. An electrolytic decomposition reaction is a type of decomposition reaction in which the activation energy for decomposition is provided in the form of electrical energy. 2H2O 2H2 O2.
C 3 H 8 C 3 H 4 2 H 2. A single substance reacts to make multiple substances. A decomposition reaction is a chemical reaction in which some chemical bonds in a compound are broken and simpler substances are formed.
The general equation for the reaction is AB A B Substance AB decomposes or breaks apart producing substances A and B. Image to be added soon. AB ----- A B.
When a compound is heated its atoms move about. NaCl since Na is positive 1 and Cl is minus one O 2 since oxygen is a. In a decomposition reaction a chemical substance is broken down into simpler substances.
A reaction in which a compound is seperated into smaller chemical species. Decomposition can be achieved by 1. Updated January 12 2019 A decomposition reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which one reactant yields two or more products.