Stunning Chemical Equation For Aerobic
This equation also showcases the process of aerobic respiration and tells us that energy of about 2900 kJ is generated when a single mole.
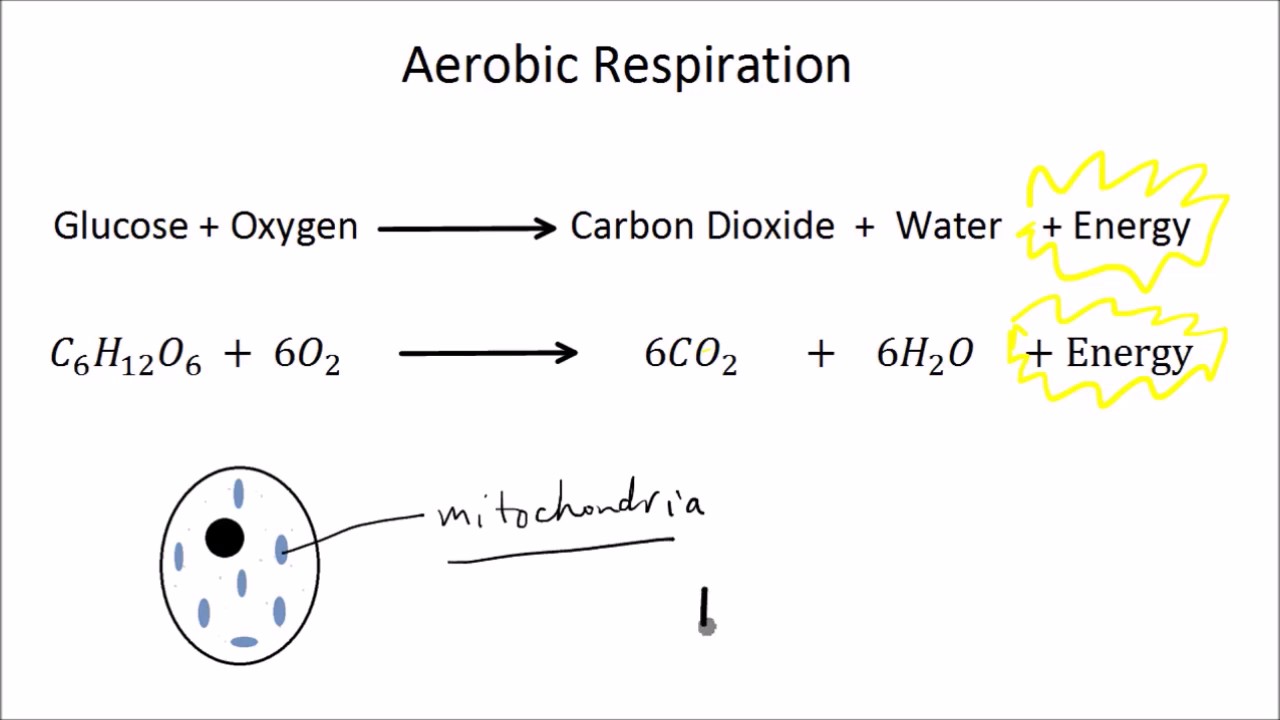
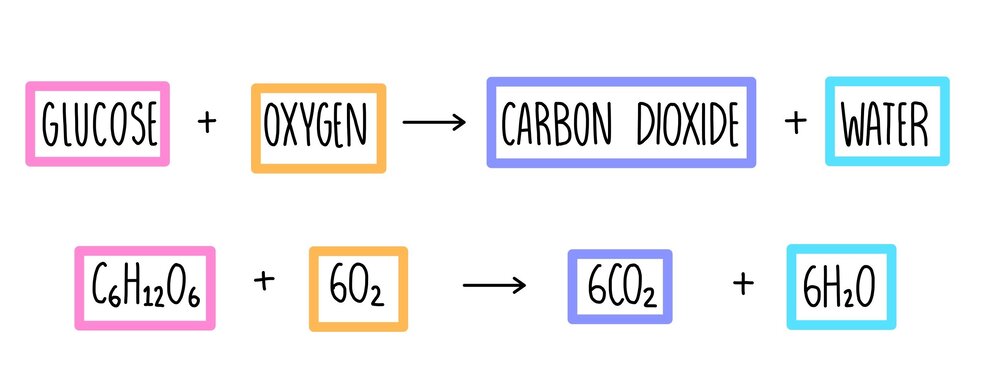
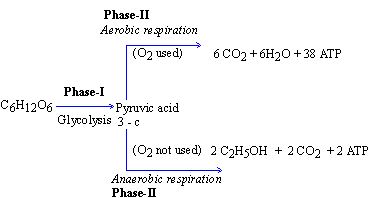
Chemical equation for aerobic. C 6 H 12 O 2 6 O 2 6 CO 2 6 H 2 O approximately 38 ATP Translating that formula into English. The chemical equation is C6H12O6 6O2 6CO2 6H2O glucose oxygen - carbon dioxide water. Hero ImagesHero ImagesGetty Images.
Glucose oxygen carbon dioxide water energy released. C6H12O6 6O2 6CO2 6H2O. C_6H_ 12O_66O_2 Rightarrow 6CO_26H_2O38ATP C 6.
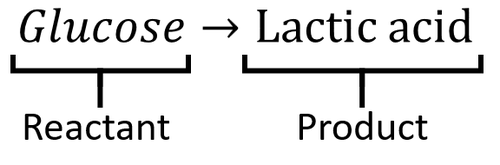
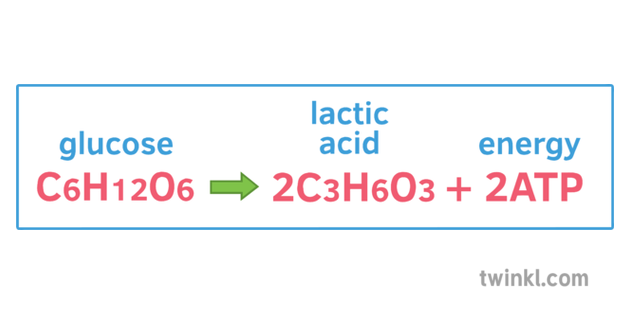
C 6 H 12 O 6 6O 2-----à 6CO 2 6H 2 O 2900 kJmol. C6H12O6 2 NAD 2 ADP 2 P ----- 2 pyruvic acid CH3COCOOH 2 ATP 2 NADH 2 H. C 6 H 1 2 O 6 6 O 2 6 C O 2 6 H 2 O 3 8 A T P.
C 6 H 12 O 6 6O 2 yields 6CO 2 6H 2 O energy as ATP. Ozone is a strong oxidant and has an oxidation potential greater than that of hydrogen peroxide. The overall reaction is.
Ozone is also 10 times more soluble in water than pure oxygen and about half of dissolved ozone introduced into the subsurface decomposes to oxygen. Oxygen enters plant cells through the stomata. Glucose C 6 H 12 O 6 is oxidized to produce carbon dioxide CO 2 and oxygen O 2 is reduced to produce.
The simplified equation for glycolysis is. Aerobic respiration takes place in the mitochondria and requires oxygen and glucose and produces carbon dioxide water and energy. Aerobic respiration is the aerobic catabolism of nutrients to carbon dioxide water and energy and involves an electron transport system in which molecular oxygen is the final electron acceptor.