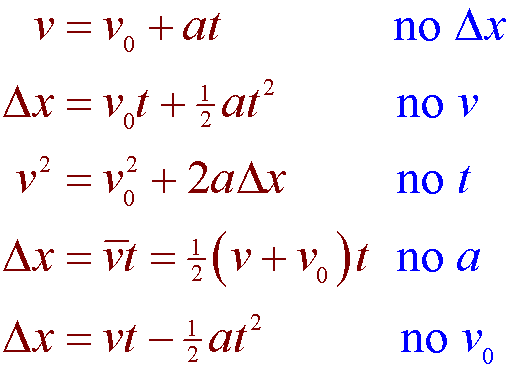Divine Kinematic Equations Of Motion

These equations link five kinematic variables.
Kinematic equations of motion. When an object motion problem falls into these categories we may use the kinematic equations to solve it. In this video we will learn the four kinematics equations. These three equations of motion govern the motion of an object in 1D 2D and 3D.
First Equation Of Motion. Instead of differentiating velocity to find acceleration integrate acceleration to find velocity. 1 List what quantities are given - will be 3 2 List what is being asked for - will be 1.
In the above equations the symbol d stands for the displacement of the object. A cool way to visually derive this kinematic formula is by considering the velocity graph for an object with constant accelerationin other words a constant slopeand starts with initial velocity as seen in the graph below. Motion is described in terms of displacementx time t velocityv and accelerationa.
Kinematic is a branch of classical mechanics which is also known as Geometry of Motion. Kinematic equations are linked with five variables which are listed below. From this we can Drive kinematic definition Kinematic is the Study of two or more object point without considering the causes of these objects or points.
Kinematic Equations for Linear Motion For constant acceleration ONLY To select the appropriate equation to solve a particular problem. Constant velocity Average velocity equals the slope of a position vs time graph when an object travels at constant velocity. Kinematic variables including position velocity acceleration of the body can be used to describe the state of rest or motion of the body.
Displacement when object moves with constant velocity. The derivation of the equations of motion is one of the most important topics in Physics. In circumstances of constant acceleration these simpler equations of motion are usually referred to as the SUVAT equations arising from the definitions of kinematic quantities.