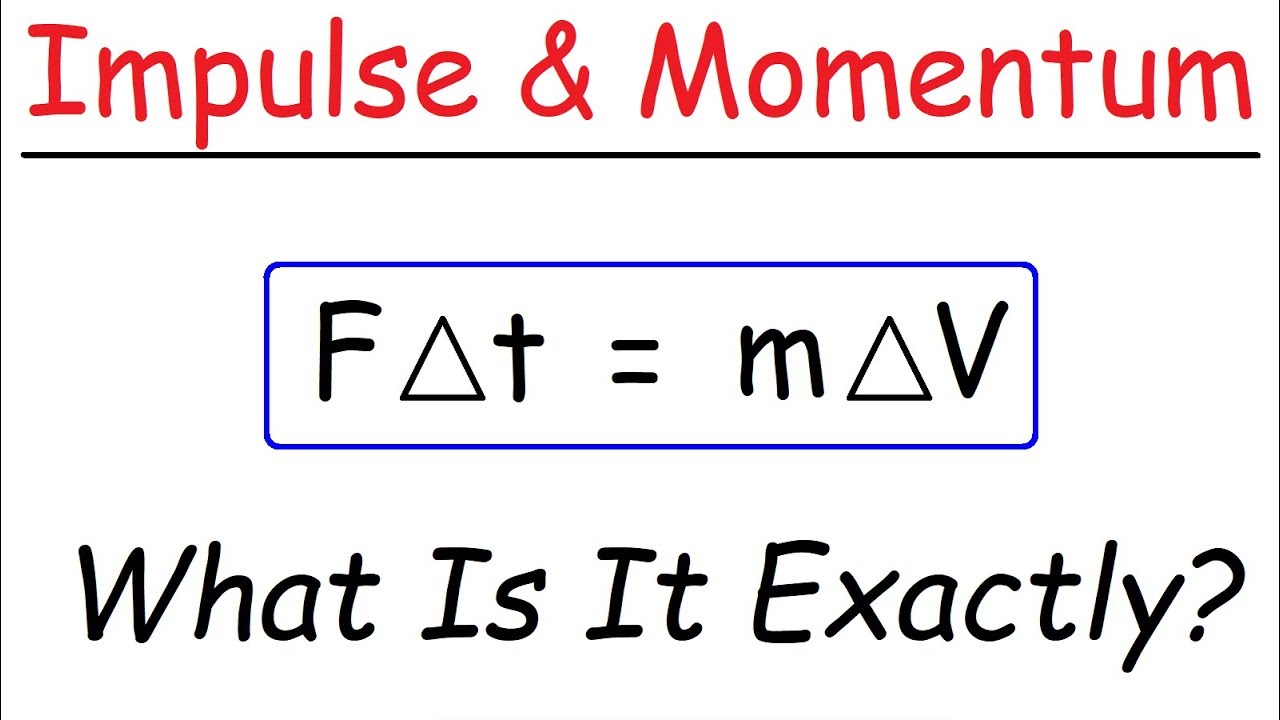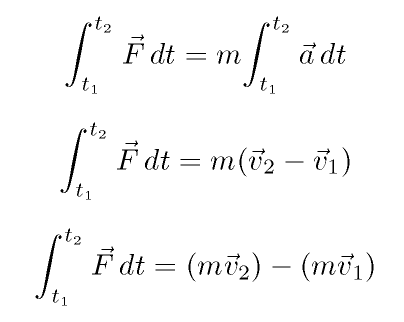Heartwarming Impulse Momentum Theorem Formula

Lets take a look at the impulse momentum theorem in action.
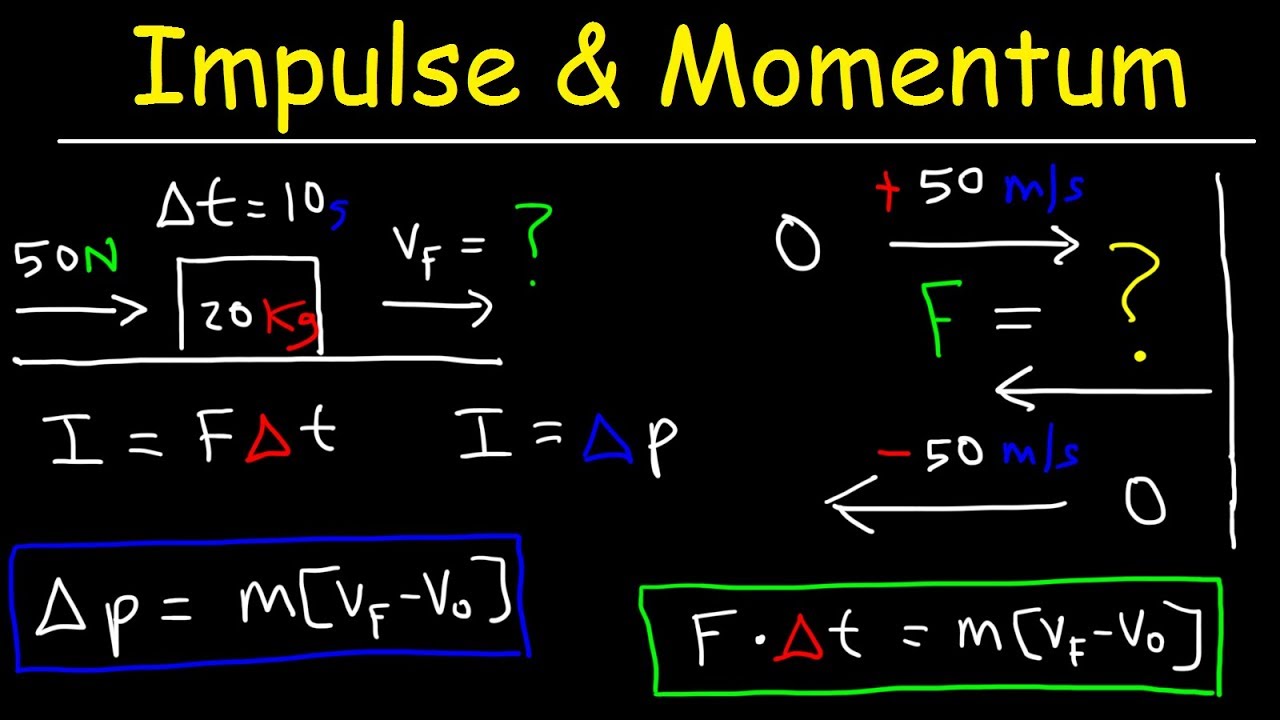
Impulse momentum theorem formula. Impulse-momentum formula The Impulse-momentum formula is obtained from the impulse-momentum theorem which states that change in momentum of an object is equal to impulse applied on the object. What Does the Impulse Momentum Theory State. The airbag causes the same change in momentum and hence the same impulse but spreads the impulse out over a.
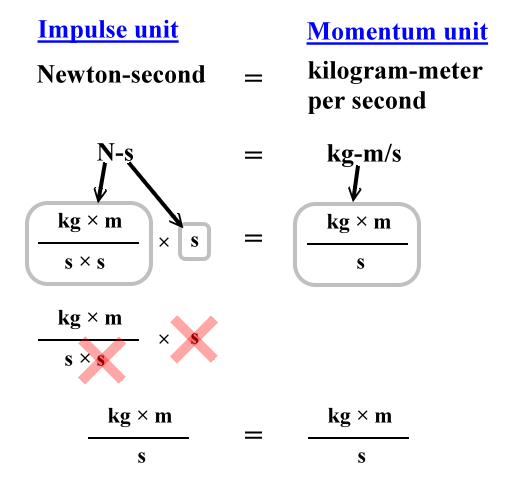
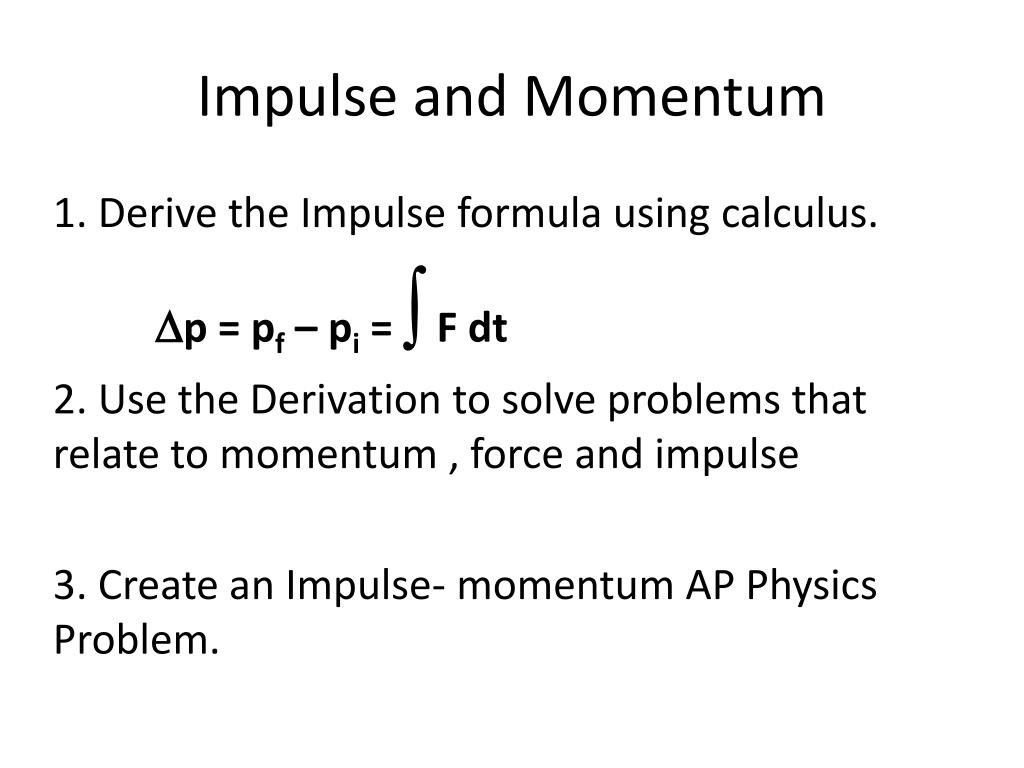
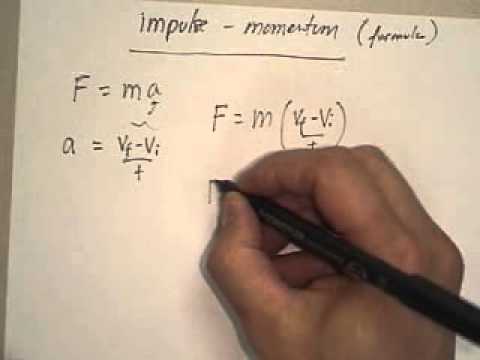
I m p u l s e F o r c e t i m e. Below we derive impulse from the equation F ma which comes from Newtons second law of motion. Impulse momentum theorem states that the change of momentum of a body is equal to the impulse applied to it.
Impulse is equal to the change in momentum of an object. The entire equation is known as the impulse-momentum theorem. A smaller resultant force must be applied for longer to bring about the same change in momentum.
From the equation we see that the impulse equals the average net external force multiplied by the time this force acts. Thus the formula to calculate the impulse can be given as. The formula is given as follows.
Impulse is equivalent to a change in momentum This can be mathematically written as- The left-hand side of the equation clearly says that Force is multiplied by time to give impulse. The impulse momentum theory takes these definitions into account and states that the change in momentum of an object equals the impulse that is applied to it. Thus if is reduced must be increased ie.
Impulse is a vector with both a value and a direction and is represented by the symbol. The Impulse-Momentum Theorem finds use in many different daily situations but it is particularly noticeable as the reason for airbags in automobiles. It is equal to the change in momentum.