Stunning Formula Of Range In Physics

Learn how to derive the Range of Projectile.
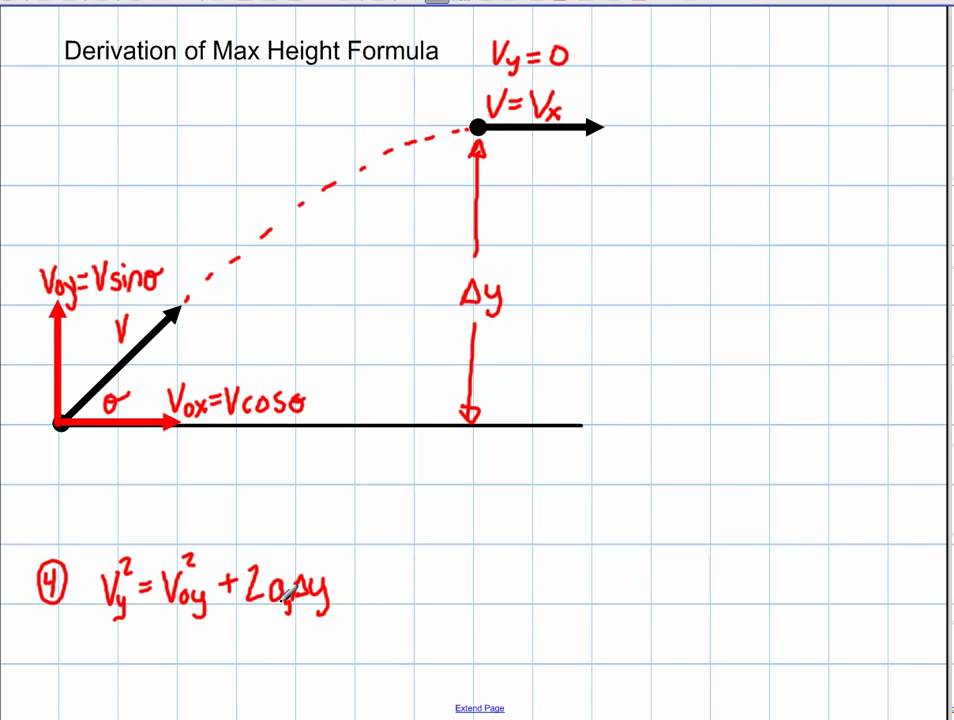
Formula of range in physics. The range of the motion is fixed by the condition y 0 y 0. It is used to determining the center of the data set and how varied the data set is from the center of the data. Using this we can rearrange the parabolic motion equation to find the range of the motion.
This horizontal range is given by the relation textHorizontal RangetextHorizontal velocitytimes texttime of flight So the formula for the horizontal range is Rfracv_02 sin 2theta_0g qquad 1. HorizontalRangeRfracu2sin 2Theta g Maximum Height. The Horizontal Range of a Projectile is defined as the horizontal displacement of a projectile when the displacement of the projectile in the y-direction is zero.
A x 0 v x v 0x x v 0xt a y g v y v 0y gt y v 0yt 1 2 gt2 where v 0x v 0 cos v 0y v 0 sin Suppose a projectile is thrown from the ground level then the range is the. Therefore in a projectile motion the Horizontal Range is given by R. Projection angle θ 0.
The following applies for ranges which are small compared to the size of the Earth. The range of an object in projectile motion means something very specific. Physics Formulas Trajectory Formula.
It is derived using the kinematics equations. Waves and Optics v λf v wavevelocity λ wavelength f frequency This formula relates the wave-length and the frequency of a wave to its speed. It may be more predictable assuming a flat Earth with a uniform gravity field and no air resistance.
We know that the horizontal range of a projectile is the distance traveled by the projectile during its time of flight. If the distance between the planet and the Earth is 63 1010m calculate the velocity of the signal. Besides we are going to discuss trajectory trajectory formula its derivation and solved examples.