Perfect Centripetal Acceleration Derivation

It is a property of the motion of the body traversing a circular path.
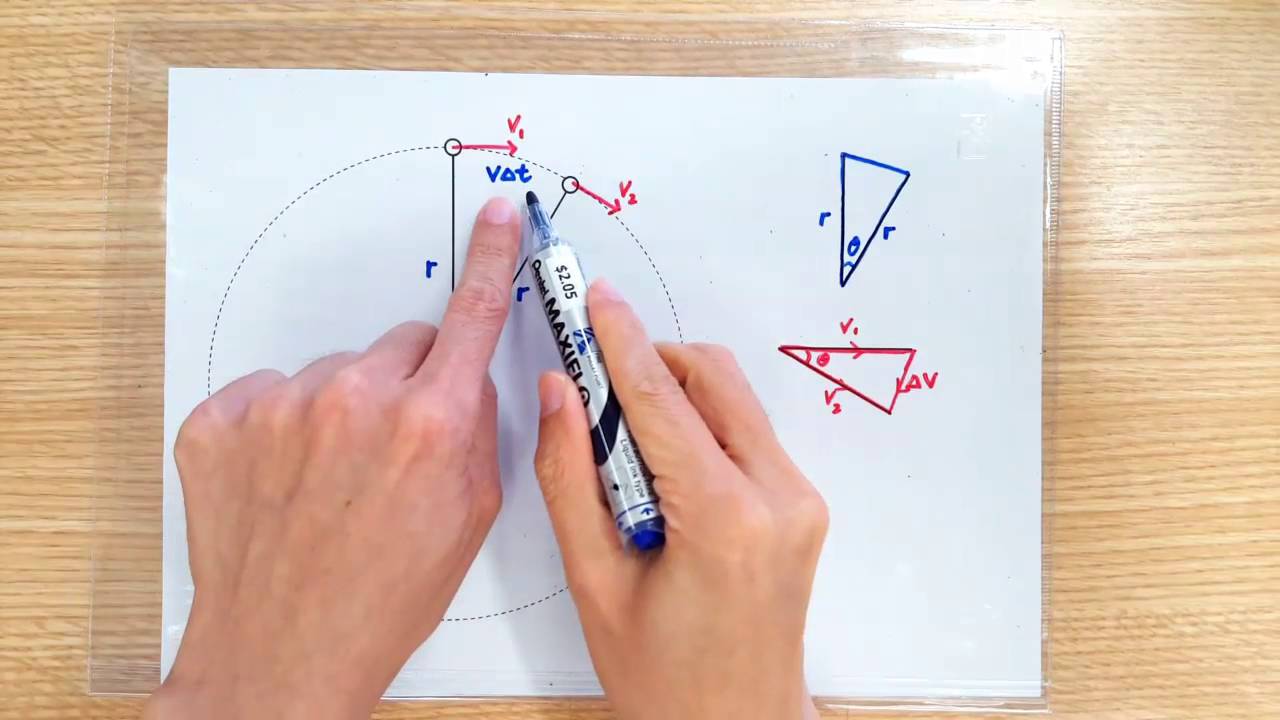
Centripetal acceleration derivation. What is the centripetal force on an object in circular motion. Because Δθ is very small the arc length Δs is equal to the chord length Δr for small time differences The direction of centripetal acceleration is toward the center of curvature but what is its magnitude. Book Search tips Selecting this option will search all publications across the Scitation platform Selecting this option will search all publications for the PublisherSociety in context.
Radius of centripetal acceleration. In the classical case plugging the centripetal acceleration a v2R gives R mv eB 6cm. Mungan Fall 2001 Consider a particle executing uniform circular motion UCM.
Derivation of Centripetal Acceleration Acceleration that acts on the object in a circular motion is called the centripetal acceleration. 000 Introduction 102 Where centripetal acceleration comes from 436 Deriving the Direction of Centripetal Acceleration 846 Deriving the Equation for Centripetal Acceleration Thank you to Mrs. Formal Derivation of Centripetal AccelerationCE.
10 For the relativistic case since the electron moves in a circle at constant speed we can take out of the derivative when we write this in terms of the speed. We derive both the direction and the equation for centripetal acceleration. The fact that the speed υ is constant means that the angle θ that the position vector r makes with the x-axis increases linearly with time.
Ac is called centripetal acceleration. Polar coordinates Adding vector components Derivatives Product Rule Chain Rule Implicit Differentiation Derivatives of sine and cosine. What I want to do in this video is a calculus proof of the famous centripetal acceleration formula that tells us the magnitude of centripetal acceleration the actual direction will change its always going to be pointing inwards but the magnitude of centripetal acceleration is equal to the magnitude of the velocity squared divided by the radius I want to be very clear this is a scalar formula.
Centripetal force is the name given to any force which causes a change in direction of velocity toward the center of the circular motion. In the time interval Δt the object traveled from point A to point B traversing through an angle of magnitude θ and along an arc of length s as shown in the following diagram. M dv dt evB.